Rural entrepreneurs exhibit worse responses to algorithmic changes, negatively impacting the efficacy of platform governance.
This blog is written by Wesley Koo and Chuck Eesley.
In many countries, rural areas have long been experiencing a troubling pattern of brain drain, leading to a dearth of business and employment opportunities. Meanwhile, in some parts of the world, the rise of digital platforms has created a path for rural entrepreneurs to earn a living through online selling.

It is one thing for entrepreneurs, whether urban or rural, to create and operate an online store, as some platforms have made it relatively easy to manage an online store – even by using just a smartphone. One troublesome aspect of online selling is that platforms frequently tweak their algorithms. This requires entrepreneurs to keep up with these changes and constantly adjust their strategy. If not, their products may not surface in customer searches.
The next problem is that platforms do not always communicate the changes in the most straightforward manner, leading to confusion among entrepreneurs. As we show in a recent paper, compared to rural entrepreneurs, urban entrepreneurs have access to offline sources of information that helps them “see through the veil”. This advantage can lead to lasting gaps in performance, especially after a major algorithmic change.
The Offline Interface for Online Platforms
For online business and digital platforms, our research highlights the importance to understand the offline interface – a term we use to describe the local, offline factors (be it economic, social, cultural or political) that affect participants’ ability to navigate a digital environment. This concept can be illustrated using the example from our paper, which explores how entrepreneurs respond to a major algorithmic change on a prominent e-commerce platform in China.
On e-commerce platforms, entrepreneurs usually start out as scavengers, either making their own products or pulling excess supplies from their environment (e.g., local factories). You see this phenomenon on platforms in both developing and developed countries. Entrepreneurs sourcing from nearby sources might sell socks, car radios and baby products, whatever assortment of products they manage to line up – or figure out what might sell based on a recent fad.
In May 2013, the platform examined in our paper was trying to increase the professionalism of its sellers (entrepreneurs) by encouraging them to specialize in a single product category. The goal was simple from the platform’s perspective: Over time, entrepreneurs would become category experts able to provide top-level customer service. To achieve this, the platform modified its algorithm to prioritize entrepreneurs who sold many products within one or two product categories (a characteristic termed “category focus”).
However, the platform had difficulty conveying this change to entrepreneurs. A somewhat cryptic announcement said that Big Data would be used to construct buyer profiles and that a new algorithm would “help entrepreneurs lock onto potential buyers and implement targeted marketing”.
Vague communication such as this is common. While hiring better communicators might help, the reality is that transferring complex information to others in a digital environment is more difficult than it seems. First, people do not always check their inboxes for platform-initiated communication. Email announcements are the poor cousins of the communications family, as they tend to be text-only. They may be crafted in a language that is poorly understood by much of the intended audience. If recipients see questions that need to be clarified, they can neither request nor receive immediate feedback.
As media richness theory has shown since the 1980s, communications that are richer in cues and more personalised, such as in-person discussions, are significantly more effective at helping decode potentially confusing messages. If we were to tell you about our research findings, we would probably do a better job sitting down and talking to you face-to-face than via this article alone.
Another reason for unclear communication is that a platform may want to hide the details of an algorithmic change – from its competitors, from public scrutiny and from participants themselves (to prevent some from “gaming the rules”).
These communication issues lead to equivocality in entrepreneurs’ interpretation of platform algorithms, and that equivocality is unevenly distributed across different segments of the entrepreneur population.
Rural entrepreneurs are left to figure things out by themselves
Let’s go back to the Chinese e-commerce platform. Based on our study of 2,395 randomly selected e-commerce entrepreneurs, the sales of rural and urban entrepreneurs were on par before the algorithm change. In fact, rural entrepreneurs, which comprised nearly 40 percent of the sample, sold a little bit more. But after the tweak, rural entrepreneurs actually went in the wrong direction by decreasing their category focus. This sank their stores’ rankings and resulted in sales that were 24 percent lower than those of their urban counterparts.
After four months, rural entrepreneurs had caught up in terms of category focus, but their sales remained inferior until several months later. This suggests that algorithms rewarded the entrepreneurs who “solved the puzzle” early, and that advantage was sustained over time.
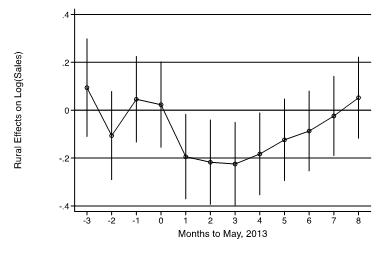
Among urban entrepreneurs, guess who were the best performers? Those nearest to the platform’s headquarters. Their category focus doubled after the algorithm change. Moreover, it is telling that the biggest predictor of an entrepreneur’s behavior was not what their same-category competitors did, but what other entrepreneurs in their physical vicinity did.
In an online environment filled with irrelevant, vague and even false information, entrepreneurs can often be led astray. In such situations, the offline interface is all the more relevant: Knowledgeable sources of information in the local environment can help entrepreneurs address points of confusion and devise the appropriate strategy. Rural entrepreneurs are not less capable than their urban counterparts, as shown by their performance before the algorithmic change. Rather, their local, offline networks just don’t give them access to the same level of help to navigate the ever-changing platform environment.
What are examples of high-quality information sources? Our field research in China showed that discussions with experts – often former platform employees or individuals connected to platform designers – were important for entrepreneurs’ success. Self-organized learning groups are also more prevalent in cities. Yet, these opportunities to acquire valuable information were less available in rural areas.
We also met rural entrepreneurs who would take a long-distance bus to cities in order to learn more about the latest platform direction. As a rural entrepreneur told us: “Oftentimes, many rule changes on the platform are quite subtle and hard to interpret. But there are these platform gurus in Beijing, who can see through the veil. You must go on a ‘pilgrimage’ to obtain the ‘holy scriptures’ from [them].”
Lessons for platform governance
The first order of inequality in the digital economy is internet access. A number of initiatives are trying to fix this inequality, for instance the Next Billion Users projects by Google. But if we look at third-party entrepreneurs on an e-commerce platform, they theoretically have the same ability to reach all customers. Geography is not supposed to matter. Except that it does.
In practice, information asymmetry due to offline differences is common. This poses a major issue for platform governance, which is not unlike what governments face when implementing new policies or regulations.
Our research suggests that, before implementing major algorithmic changes, a platform needs to study its audiences carefully and assess their diverse information needs. Participants in remote geographic areas need special attention. This could mean creating learning groups with experts from nearby cities or sending clarifying messages or videos in a targeted manner, in which case the platform needs to implement well-designed pre-testing. The platform could also help information-disadvantaged participants by creating ranking algorithms that do not rush to punish those who fall behind on day one. In other words, algorithms that are less dependent on prior performance could better enable certain disadvantaged participants to adjust to a new platform order.
Is our research only applicable to China? Far from it. It is relevant for the planet’s 3.4 billion rural dwellers, who represent a vast pool of potential entrepreneurial talent for the digital economy. You may first think of developing countries, but most first-world economies also have rural areas that need to be revitalized. In U.S. states, such as Ohio and Kentucky, young talent leaves and hardly ever comes back. Online entrepreneurship could help lure talent, but it is important to promote a rich local information environment in these communities to nurture it. These lessons are valuable for a post-pandemic world in which an increasing number of people switch between online and offline in their work and daily routines.
This blog is based on Wesley and Chuck’s research published in the Strategic Management Journal, which is included in the platformpapers references dashboard:
Koo, W. W., & Eesley, C. E. (2021). Platform governance and the rural–urban divide: Sellers’ responses to design change. Strategic Management Journal, 42(5), 941-967.